
According to sources, Andrew Parker-Bowles, the ex-husband of Queen Camilla, is well on his way to rediscovering love with a face that most people in the UK are familiar with.
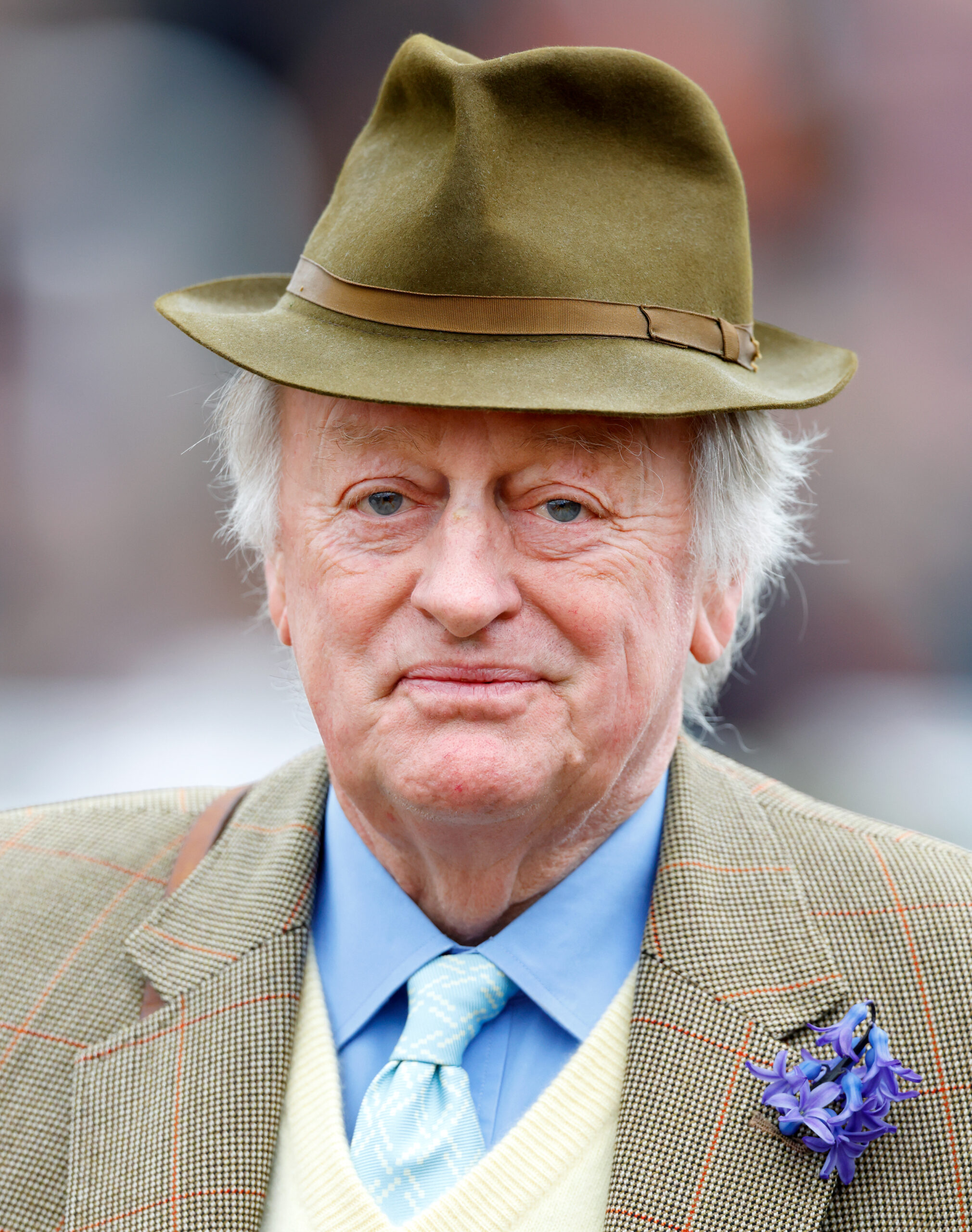
It has been reported that the 84-year-old former Royal Horse Guards officer is seeing 79-year-old TV broadcaster and actress Anne Robinson, 14 years after the death of his second wife, Rosemary Dickinson, in 2010.
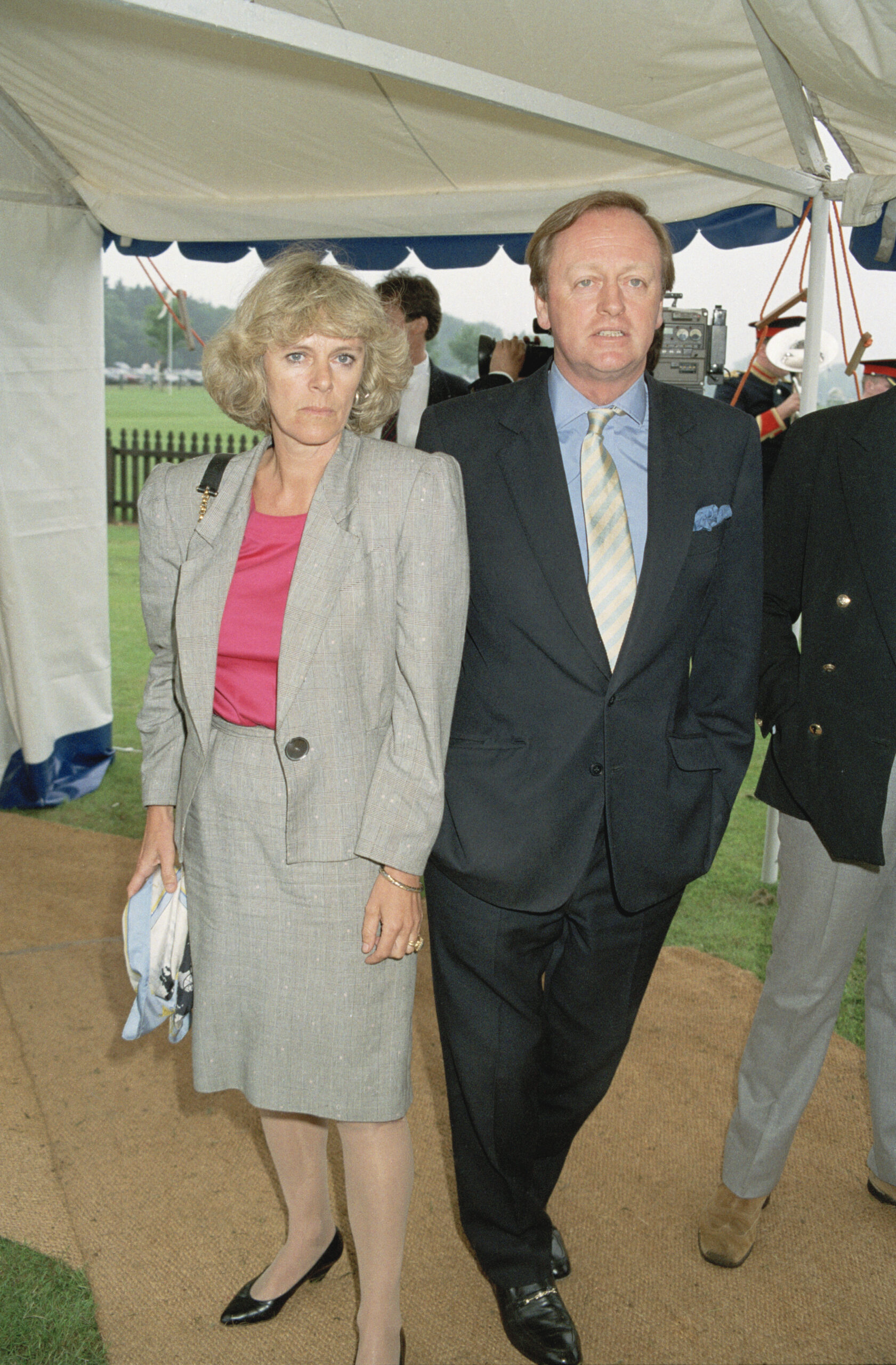
Naturally, Parker-Bowles’s first marriage—a 22-year union with Camilla, who is currently the wife of Charles, the King of England—is arguably the most well-known.
A year before the former married Rosemary Dickinson, in 1995, Andrew and Camilla got divorced, and in 2005, Camilla famously got married to Prince Charles.
It was commonly known that during his marriage to Camilla, Andrew had several extramarital encounters, some of which he had with people she regarded as friends.
Following the death of his second wife, Rosemary, Andrew’s love life has mainly flown beneath the radar until recently. 2023 saw a lot of reports implying that he was dating TV host Anne Robinson; Robinson now seems to have verified the rumors.

The journalist responded to the topic of whether or not she was romantically engaged with Camilla’s ex-husband with her customary snappiness in an open interview.
Indeed. Complete halt. “Take care of yourself,” disclosed the former host of Weakest Link.
Retired Army Brigadier Andrew and Anne reportedly reside in England’s Cotswolds. The two are claimed to have first connected over a lunch with mutual acquaintances last year, but they have mainly managed to keep their developing connection quiet since then.

Regarding Anne, the 78-year-old has been without a partner for approximately 17 years after divorcing her previous spouse, John Penrose, in 2007.
“I’d say that like everything else I’ve done, it’s always worth the risk,” she remarked of her romance with Andrew. “I really believe that taking chances might surprise you. both in a personal and professional capacity.
In fact, the majority of internet comments appear to be supportive, with people expressing gratitude that Andrew and Anne discovered one other later in life.
“We need more love stories like this, 8479,” one Facebook commenter said.
Another individual commented, “She looks better than his ex-wife and hopefully has a better personality.”
“It’s obvious he has a type,” a third individual joked.

Camilla and Charles, meanwhile, recently flew out to Aberdeen, Scotland to mark their 19th wedding anniversary. The couple was pictured in photos taken at Aberdeen Airport last month after taking a plane from London.
After the shocking news of her husband’s cancer diagnosis, Queen Camilla has been a rock for him. Her popularity among the British public has also increased since the difficult beginning of her royal career following the loss of the cherished Princess Diana.
My Late Stepmother Left Me Her $2.5 Million Vacation Home While Her Daughters Only Got $5,000 Each

For years, Carol lived in the shadow of her stepfamily, unseen and ignored. Then, out of nowhere, a lawyer’s call shattered her quiet life: her stepmother, who had barely loved her, had left Carol a $2.5 million inheritance, while her own daughters got only $5,000 each. The reason blew Carol’s mind.
When I was 12, my dad remarried his new girlfriend. Linda came into our lives with her two daughters, Amanda and Becca, who were a few years older than me. Blending into their family felt like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole. Amanda and Becca were the stars of every show — praised, adored, and always front and center.
And me? I was just… there. Like a corner table.

A newlywed couple | Source: Midjourney
I remember watching them from the edges of the room, feeling invisible. At family gatherings, I’d sit quietly, my hands folded in my lap, observing how effortlessly they commanded attention.
“Look at my daughter’s straight A’s,” Linda would beam, her eyes never finding mine. My report cards would sit forgotten on the kitchen counter, collecting dust and ignorance.
“Do you want some help with that?” I’d sometimes ask Becca when she was struggling with homework, hoping for a connection.
She’d look up, a hint of disdain in her eyes. “I’ve got it,” she’d say, turning away. Those moments crushed whatever hope I had of belonging.

An upset girl with her eyes downcast | Source: Midjourney
Linda wasn’t outright mean, but she wasn’t warm either. I wasn’t included in anything, not really. Family trips were planned around Amanda and Becca’s wants. Holidays? I spent more time washing dishes than enjoying the celebrations.
Once, when I was 16, I asked why everything had to revolve around them. Linda barely looked at me as she said, “You’re not the only one here, Carol. Stop acting like a victim.”
Her words stung then, and they still sting now.
The kitchen would become my sanctuary and my prison. While others laughed in the living room, I’d scrub plates, the sound of my family’s joy muffled by the running water. Each dish I cleaned felt like another layer of my identity being wiped away, replaced by the expectation of being the background character in my own house.

A teenage girl washing vessels | Source: Pexels
By the time I turned 18, I couldn’t take it anymore. I left for college, went no-contact with Amanda and Becca, and kept Linda at arm’s length. When Dad passed away two years later, we lost the only thing holding us together. Linda faded from my life after that.
The only other connection I had with her was through the phonebook, with my phone number scribbled on it. But she barely called, and I didn’t want her to, either.
For 15 years, I rarely thought about her. I got married to my wonderful boyfriend David, welcomed two amazing kids, and life just rolled on. Then, one day, my phone rang, and everything changed.
“Carol, this is Mr. Higgins, Linda’s attorney.”
I paused, confused. The name felt distant, like an echo from a life I’d deliberately forgotten. “Okay… why are you calling me?”
“I’m sorry to inform you that Linda passed away last week from lung cancer,” he said gently.

A woman holding a smartphone | Source: Midjourney
For a moment, I was too stunned to respond. Memories flickered like old photographs: Linda’s dismissive glances, her quick corrections, and the perpetual distance between us.
I hadn’t even known she was sick. The irony wasn’t lost on me. We’d been so disconnected that even her terminal illness had slipped past me completely.
“I see,” I finally managed. “What does this have to do with me?”
“She named you in her will. Linda left you her vacation home.”
My heart skipped a beat. “Her vacation home?”
“Yes, the one that belonged to your father and was passed on to her after his death. It’s valued at $2.5 million,” he explained. “Her daughters Amanda and Becca were left $5,000 each.”

A startled woman holding a phone | Source: Midjourney
I sat down hard on the couch, my head spinning. The numbers seemed surreal.
All those years of feeling like an afterthought, and now this? Linda had barely been a presence in my life, yet she’d left me her most valuable asset and almost nothing for her own daughters. Why?
Before I could process it, my phone buzzed with incoming texts. The screen lit up with family drama, as if Linda’s death had suddenly reignited old tensions.
My husband, David, leaned over to read one of them. His jaw tightened. “Amanda’s accusing you of manipulating Linda. Classy!”
“She’s calling me a thief,” I said, staring at the words. The accusation felt achingly familiar… the same dismissive tone I’d heard throughout my childhood, the same narrative of me being the problem.

An upset woman | Source: Midjourney
“That’s nothing,” he muttered, scrolling through Becca’s online post. “She’s ranting about ‘backstabbers destroying families.’”
A bitter laugh escaped me. Destroy families? We were barely a family to begin with. Those connections had been threadbare, held together by nothing more than shared last names and occasional holiday gatherings.
I sighed, setting my phone aside. “Why would Linda do this? We weren’t even close.”
David shrugged, his eyes soft with understanding. “Maybe you need to find out.”
I nodded. Something told me this inheritance was more than just a financial transaction. It felt like an unfinished story, waiting to be understood. So, I decided to dig through the house to see if I could find any clues.

A woman standing before a mansion | Source: Midjourney
The vacation home looked exactly as I remembered when I entered. Nestled on the edge of a serene lake, it had always been my dad’s favorite place. We used to fish on the dock for hours, talking about everything and nothing.
Standing in the doorway, I felt like a ghost of my former self. Each step was a journey through time, my fingers tracing familiar surfaces, collecting memories like dust.
Dad would sit in that worn armchair by the window, his fishing hat tilted just so, telling me stories about his childhood. Those moments had been our sanctuary… a place where I felt truly seen and loved.
I walked through the house, memories washing over me with every step. The living room still had the same luxurious furniture. The smell of cedar lingered, just like it did years ago.

A grand living room | Source: Midjourney
But I wasn’t here for nostalgia. I needed answers. Linda was meticulous, and I hoped somewhere in her files, she’d left a clue about her decision. Each drawer I opened felt like peeling back layers of a complicated family history.
Finally, tucked away in the back of a drawer in her office, I found a letter addressed to me. The paper was crisp, the envelope sealed with a precision that was quintessentially Linda.
My hands trembled slightly as I reached for it, knowing that this small piece of paper might hold the key to understanding everything.

A woman holding an envelope | Source: Midjourney
With anxious eyes, I began reading:
“Dear Carol,
By the time you read this, I hope you’ll understand the choice I made.
I’ve carried the weight of my mistakes for years, and this letter is my final attempt to make things right. The truth is, I failed you… repeatedly and profoundly. When I married your father, I was so focused on protecting Amanda and Becca that I became blind to the harm I was causing you.
My insecurities after my divorce turned me into a mother who couldn’t see beyond her own fears. I created a hierarchy in our family where you were always last, always invisible. I watched you endure our family’s coldness, and I did nothing.
Time has a way of revealing uncomfortable truths. I’ve seen Amanda and Becca for who they truly are… entitled, manipulative women who learned to value status over genuine connection. And you? You built a life of integrity without seeking my validation or approval.
This house, the place your father loved most, was always meant to be a sanctuary. He spoke of your times here with such joy and love. I realize now that I robbed you of those precious memories, of feeling truly part of a family.
The vacation home is my apology. Not just a piece of property, but a chance for a fresh start. A legacy from a father who loved you completely, and a mother who is finally, painfully aware of her mistakes.
Forgive me, if you can.
Linda”

A shocked woman holding a letter | Source: Midjourney
Tears blurred the words. My hands trembled, not from anger, but from a profound sense of loss for the relationship we never had, and for the years wasted in silence and misunderstanding.
I read the letter twice, then for a third time, and I let her words sink in. She’d known all along how unfair she’d been but hadn’t found the courage to fix it while she was alive. The letter felt like a final, desperate attempt at redemption and a whispered apology from beyond.
Outside, the lake sparkled, indifferent to the complex emotions swirling inside me. Dad’s favorite place. My sanctuary. Now, unexpectedly, my inheritance.
A week later, I got another call from Linda’s lawyer.

A lawyer talking on the phone in his office | Source: Pexels
“There’s a secondary clause in Linda’s will,” he explained. “She set aside a $5 million trust for Amanda and Becca.”
I felt my stomach tighten. “I’m guessing there’s a catch?”
He hesitated, and in that pause, I could almost hear Linda’s calculated precision. “They’d only inherit it if they accept the terms of the will without any hostility toward you.”
“And if they don’t?”
“The funds will be donated to a local youth charity Linda supported,” he said. “Given the phone calls, social media posts, and emails from Amanda and Becca, the trust has been forfeited.”

A woman talking on the phone | Source: Pexels
I was floored. Linda had anticipated Amanda and Becca’s behavior and planned accordingly. It was like a final chess move, calculated and precise. The lawyer confirmed the charity would receive the money instead.
A part of me wanted to laugh at the irony. Linda, who had spent years marginalizing me, had ultimately chosen to protect me in the most unexpected way possible.
Amanda called me that evening, and she was so furious. “You think you’ve won? You’re disgusting! You stole everything from us!”
I stayed calm, years of being overlooked had taught me emotional resilience. “I didn’t steal anything, Amanda. Maybe you should think about why Linda made the decisions she did.”
She hung up on me without saying much. But I could feel her fury.

An angry woman talking on the phone | Source: Pexels
That night, David and I sat on the porch of the vacation home. The lake was calm, the sky painted with soft hues of pink and orange. Memories of fishing with my dad danced across the water’s surface, bringing a bittersweet smile to my lips.
“Do you feel guilty?” David asked, breaking the silence.
I thought about it, watching a lone bird glide across the darkening sky. “Not really. But I feel… sad. She waited too long to try and make things right. If she’d just talked to me while she was alive, maybe things could’ve been different.”
David nodded, understanding etched in the gentle pressure of his arm around my shoulders. “She didn’t know how to fix things, so she did what she could in the end. It’s not perfect, but it’s something.”

A couple embracing each other | Source: Unsplash
The lake seemed to whisper in agreement, its gentle waves a subtle reminder that healing isn’t always straightforward.
Amanda and Becca have gone no-contact, and honestly, it’s a relief. The vacation home is ours now, and David and I are planning to move here next year with our kids. The house feels less like an inheritance and more like a homecoming.
Linda may not have been the mother I wanted, but her final act was both an apology and a gift… a chance to reclaim a piece of my history.
And that, at least, is something.
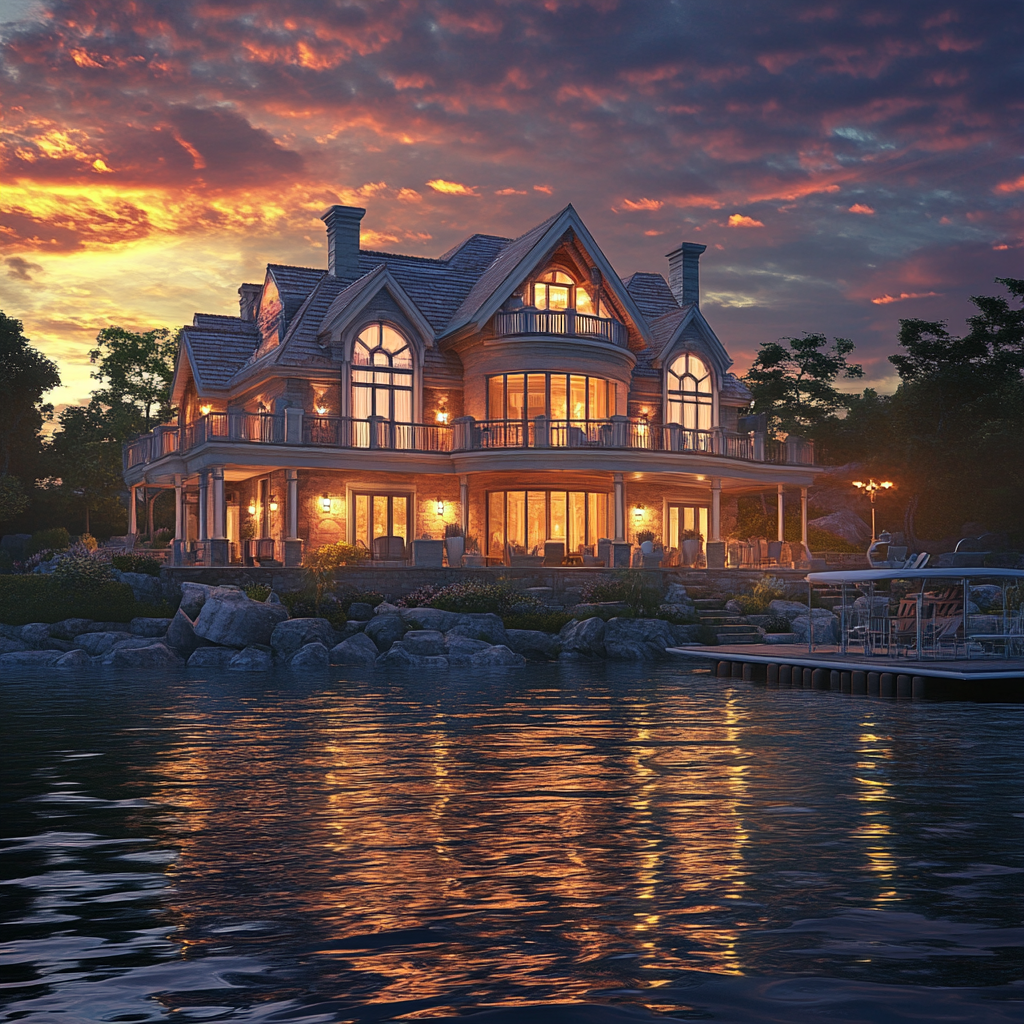

A magnificent house by the lake | Source: Midjourney
This work is inspired by real events and people, but it has been fictionalized for creative purposes. Names, characters, and details have been changed to protect privacy and enhance the narrative. Any resemblance to actual persons, living or dead, or actual events is purely coincidental and not intended by the author.
The author and publisher make no claims to the accuracy of events or the portrayal of characters and are not liable for any misinterpretation. This story is provided “as is,” and any opinions expressed are those of the characters and do not reflect the views of the author or publisher.


Leave a Reply