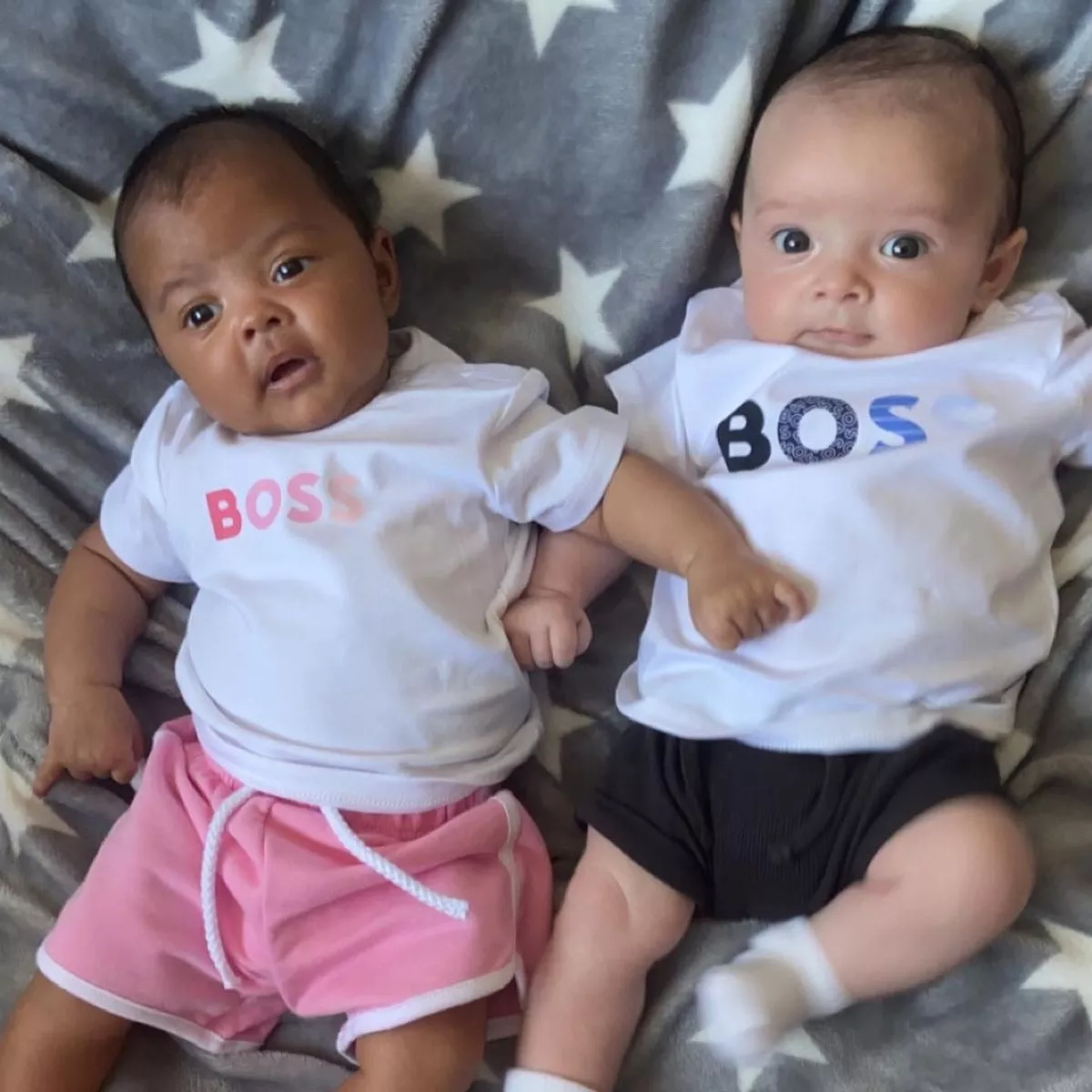

In April 2022, Englishwoman Chantelle Broughton, 29, gave birth to twins, Azirah and Ayon. The twins looked exactly alike at first, but as they developed, some noticeable distinctions became apparent.
While Ayon’s complexion remained pale and his eyes remained a stunning blue, Azirah’s skin darkened and her eyes took on a warm brown hue. Their mother found these shifts fascinating and felt that they emphasized the special qualities of their development.

Because of their multiple racial backgrounds, Chantelle and her husband’s children have a diversified genetic make-up. While Chantelle’s paternal grandfather was Scottish and had Jamaican connections, her maternal grandfather was Nigerian. The twins’ unique physical characteristics were impacted by their multiracial ancestry.
Because of the twins’ dissimilar looks, Chantelle frequently gets questions from people while the family is out. Even though they are identical twins, Azirah and Ayon have different personalities: Azirah is quiet and obedient, whilst Ayon is energetic.

According to experts, differences in the color of a twin’s skin and eyes can be caused by genetic factors, especially in families where one of the parents is not white. Ayon and Azirah exhibit astonishing and gorgeous diversity, which is the result of unusual genetic pairings in Chantelle’s family.

Mulher odiava a sogra até que um dia sua vida virou de cabeça para baixo — História do dia

O casamento de Mary com Ed teve um preço: sua mãe Scarlett, que nunca escondeu seu desdém. De insultos no dia do casamento a críticas constantes, Scarlett parecia determinada a dificultar a vida de Mary. As tensões aumentavam a cada visita… até que algo ainda mais chocante aconteceu.
Mary e seu marido, Ed, dirigiram em silêncio em direção à casa de sua mãe, Scarlett. Embora ainda não tivessem chegado, Mary já estava ansiosa pela viagem de volta. Scarlett, afinal, simplesmente a desprezava.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
No casamento deles, Scarlett até apareceu usando um véu; Mary ficou grata por não ter chegado com um vestido de noiva completo. Scarlett era uma daquelas mães que não conseguiam deixar seu “menininho”, não importa o quão crescido ele fosse.
Quando eles entraram na garagem, Mary saiu relutantemente, seguindo Ed. Ela respirou fundo, se preparando para qualquer insulto mais recente que Scarlett tivesse guardado.
Forçando um sorriso, ela se preparou, esperando que sua expressão a levasse através desta visita. Scarlett abriu a porta com um largo sorriso e imediatamente envolveu seus braços em volta de Ed.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Oh, meu bebê! Você finalmente chegou! Senti sua falta mais do que você imagina!” ela exclamou, segurando-o perto.
“Mãe, faz só uma semana”, respondeu Ed, saindo do abraço dela.
Scarlett lançou um breve olhar para Ed antes de virar seu olhar para Mary, sua expressão mudando. “Bem, Mary, vejo que você ganhou alguns quilos,” ela disse com um sorriso.
Mary soltou um suspiro baixo, resistindo à vontade de responder. Ela forçou um sorriso tenso em vez disso. “É bom ver você também, Scarlett.”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
O jantar pareceu interminável enquanto Scarlett se lançava em sua lista habitual de reclamações. “Mary não sabe cozinhar. Ela não trabalha em um lugar respeitável. Ela nem sabe se vestir direito”, Scarlett declarou, lançando olhares rápidos para Ed em busca de apoio.
Mary agarrou o garfo com força, mordendo a língua. Ela sabia que qualquer resposta só colocaria lenha na fogueira de Scarlett. Mas então Scarlett disse algo que fez a paciência de Mary acabar — palavras mais afiadas do que qualquer coisa antes.
Scarlett olhou para o outro lado da mesa, seus olhos fixos em Mary. “Bem,” ela disse lentamente, “acho que já passou da hora de você me dar um neto. Ou talvez,” ela acrescentou com um sorriso, “Mary tenha… alguns problemas?”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
O coração de Mary afundou. Eles estavam tentando ter um bebê há seis meses sem sucesso, e as palavras de Scarlett ardiam como sal em uma ferida. “Como você ousa!”, Mary explodiu. “Pare de se intrometer em nossas vidas! Talvez seja seu filho que tenha o problema!”
Scarlett se recostou, estreitando os olhos. “Isso é absurdo! Meu filho é perfeitamente saudável, muito obrigada. Mas você, Mary… quem sabe o que você estava fazendo antes de conhecer Eddie?”
O rosto de Mary ficou vermelho de raiva. “Você é uma maldita bruxa!” ela gritou, sua voz tremendo. Ela se virou para Ed, que não tinha dito uma palavra. “Você vai ficar sentado aí e deixá-la dizer isso?”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Scarlett lançou um olhar penetrante para o filho. “Sim, Eddie, diga à sua esposa louca para mostrar algum respeito,” ela disse, seu tom debochado.
Ed deu de ombros, ainda rolando o celular. “Resolvam vocês mesmos.”
Scarlett se inclinou em direção a Mary, sua voz baixa. “Minha vizinha mencionou chás de ervas. Ela jura que eles ajudam pessoas como você.”
Mary abriu a boca para retrucar, mas sentiu uma onda repentina de náusea. Ela apertou o estômago, forçando as palavras a saírem. “Por que você não… bebe seu próprio chá?”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Incapaz de se segurar, Mary correu para o banheiro. Quando voltou, ainda pálida, olhou para Ed. “Quero ir para casa.”
“Ok”, ele disse, mal erguendo os olhos.
Scarlett inclinou a cabeça, um olhar falso de preocupação cruzando seu rosto. “O que há de errado? Você está se sentindo mal?”
Os olhos de Mary se estreitaram. “Você provavelmente me envenenou,” ela murmurou, cansada demais para continuar discutindo.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
No caminho para casa, a mente de Mary correu. Ela tinha que ter certeza. “Ed, você pode passar na farmácia?”, ela perguntou calmamente.
Ele suspirou, mas entrou no estacionamento. Ela correu para dentro, pegou um teste de gravidez e pagou rapidamente. De volta a casa, ela foi direto para o banheiro. Prendeu a respiração, esperando. Então, os resultados apareceram — duas linhas. Ela engasgou, sentindo uma onda de excitação e alívio.
Ela correu para mostrar a Ed, seu rosto brilhando. “Ed, nós vamos ter um bebê!”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Ed olhou para o teste, sua expressão ilegível. “Oh. Isso é… bom,” ele murmurou, mal encontrando os olhos dela.
O coração de Mary afundou um pouco. Ela estava muito feliz, mas a reação de Ed pareceu uma sombra sobre sua felicidade.
Algumas semanas se passaram desde que Mary descobriu que estava grávida, e ela estava finalmente começando a se ajustar à ideia de se tornar mãe. Era a primeira consulta médica delas, e ela estava sentada na cama, esperando Ed terminar seu banho para que pudessem sair juntos.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Ela esperava que ele demonstrasse alguma excitação, mas ele parecia distante ultimamente, preocupado e retraído.
Enquanto esperava, o telefone de Ed vibrou ao lado dela, acendendo com uma mensagem. Normalmente, ela respeitava a privacidade dele. Mas a maneira como ele estava agindo a fez hesitar.
Sem perceber completamente, ela pegou o telefone dele. Ela tentou desbloqueá-lo e ficou surpresa ao encontrar uma senha. Ela não conseguia se lembrar dele já ter usado uma antes. Por impulso, ela tentou a data de nascimento dele. A tela desbloqueou imediatamente.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
A mensagem a encarou de volta: uma foto de uma mulher seminu, sorrindo de um jeito que fez seu estômago revirar. Abaixo da foto, uma mensagem dizia: “Mal posso esperar para ver você, baby.”
Suas mãos tremiam enquanto ela rolava a conversa, cada palavra parecendo uma nova traição. Ed havia dito a essa mulher que ele era rico, dono de uma construtora — bem diferente de seu trabalho real.
Com o coração acelerado, ela tirou capturas de tela e as salvou em seu telefone como evidência de suas mentiras e enganos.
Quando Ed saiu do banheiro, ela estava esperando, segurando o telefone dele. Seu rosto estava pálido, seus olhos cheios de mágoa e raiva.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“O que é isso?!” ela gritou, empurrando o telefone para ele.
A expressão dele ficou dura, e ele pegou o telefone da mão dela. “Não é da sua conta,” ele retrucou.
A voz de Mary se elevou, cheia de dor. “Não é da minha conta? Você está me traindo! E eu estou grávida, Ed — sua esposa grávida!”
Os olhos dele se estreitaram. “Talvez você seja quem esteja me traindo,” ele retrucou, um sorriso de escárnio se formando em seu rosto. “Como eu sei que esse bebê é meu?”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Mary sentiu seu mundo inteiro girar. “Você está falando sério? Estamos tentando há seis meses. Agora você está dizendo isso?” Sua voz falhou.
Ed cruzou os braços. “Seis meses, nenhuma sorte, e agora, de repente, simplesmente acontece? Conveniente.”
“Você está saindo com essa mulher há mais de seis meses, Ed. Eu vi tudo. Você mentiu para ela também! Disse que é rico, que tem uma empresa!” A voz de Mary tremeu.
Ed deu de ombros, friamente impassível. “Não importa. Estou pedindo o divórcio. Este casamento acabou.”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Você realmente acha que aquela mulher vai ficar por aqui quando descobrir a verdade sobre você?” Mary retrucou.
“Confie em mim, ela não vai descobrir. E quando isso acabar, eu vou ficar com essa casa e tudo o mais que você tem. Além disso, o dinheiro da minha mãe.” Ele sorriu.
A voz de Mary se elevou em protesto. “Esta casa foi comprada pelo meu pai!”
“Sim? Está em nossos nomes”, Ed respondeu com um sorriso presunçoso.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
A voz de Mary suavizou quando ela perguntou: “E o bebê?”
Ed apenas deu de ombros. “Você não pode provar que é meu até que nasça. Aí, será tarde demais.” E com isso, ele a jogou para fora, deixando-a em lágrimas.
Desesperada e magoada, Mary fez uma escolha: ir até Scarlett e mostrar tudo a ela. Scarlett tinha que saber a verdade sobre seu filho.
Ela sentou-se em frente a Scarlett, seu coração batendo forte enquanto ela lhe contava tudo — as mentiras de Ed, suas trapaças, suas ameaças de tomar a casa. Ela prendeu a respiração, esperando que Scarlett a dispensasse. Mas, para sua surpresa, ela escutou, seu rosto ficando pálido.
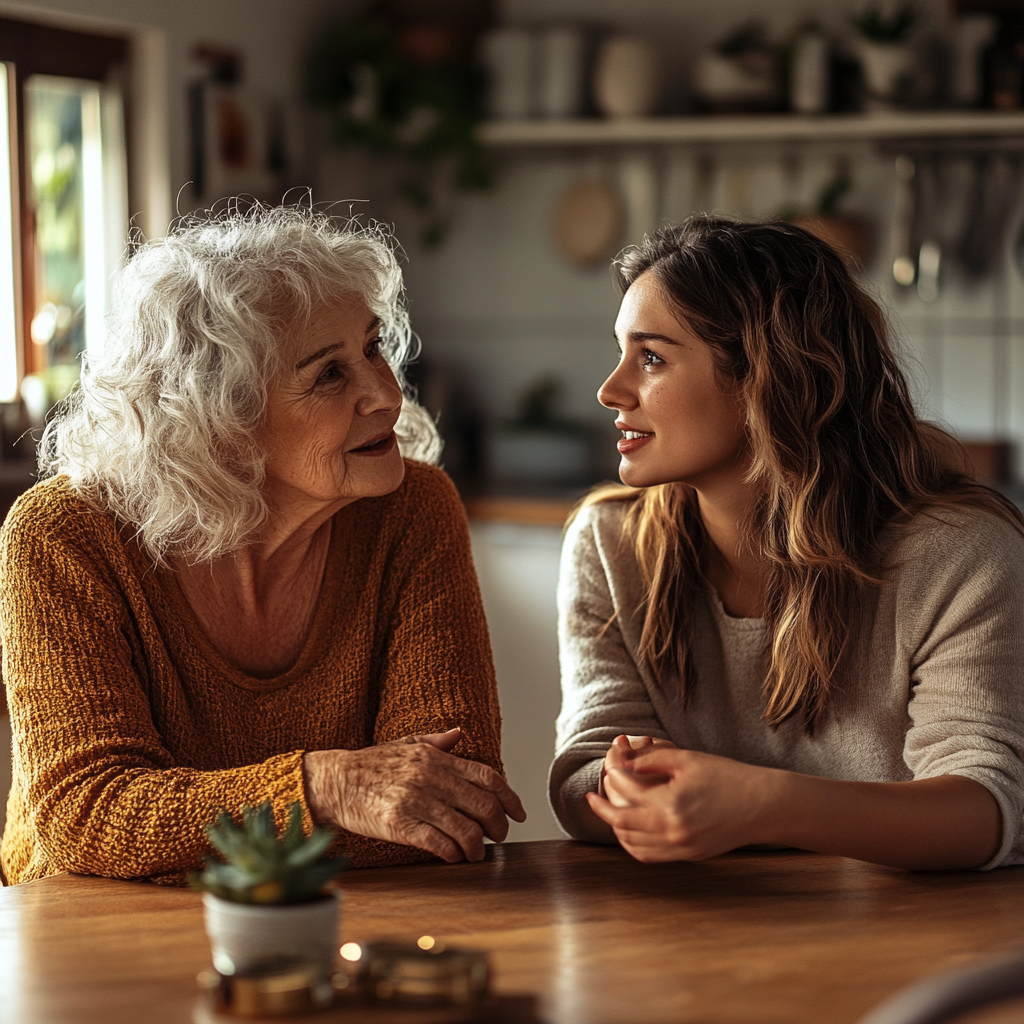

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Scarlett olhou para baixo, lágrimas brotando em seus olhos. “Ele também está tirando dinheiro de mim”, ela disse suavemente. “Cada centavo que o pai dele me deixou, tudo que eu economizei. Ele disse que precisava para consultas médicas porque você não conseguia engravidar.”
Mary balançou a cabeça, sentindo raiva e tristeza. “Ele nunca foi ao médico. Toda vez que eu tocava no assunto, ele se recusava. Eu chequei nossa conta, Scarlett. Ele tem sacado quantias enormes.”
Scarlett cerrou os punhos. “Não acredito que meu filho faria isso”, ela disse, com a voz trêmula. “Ele mentiu para nós dois.”
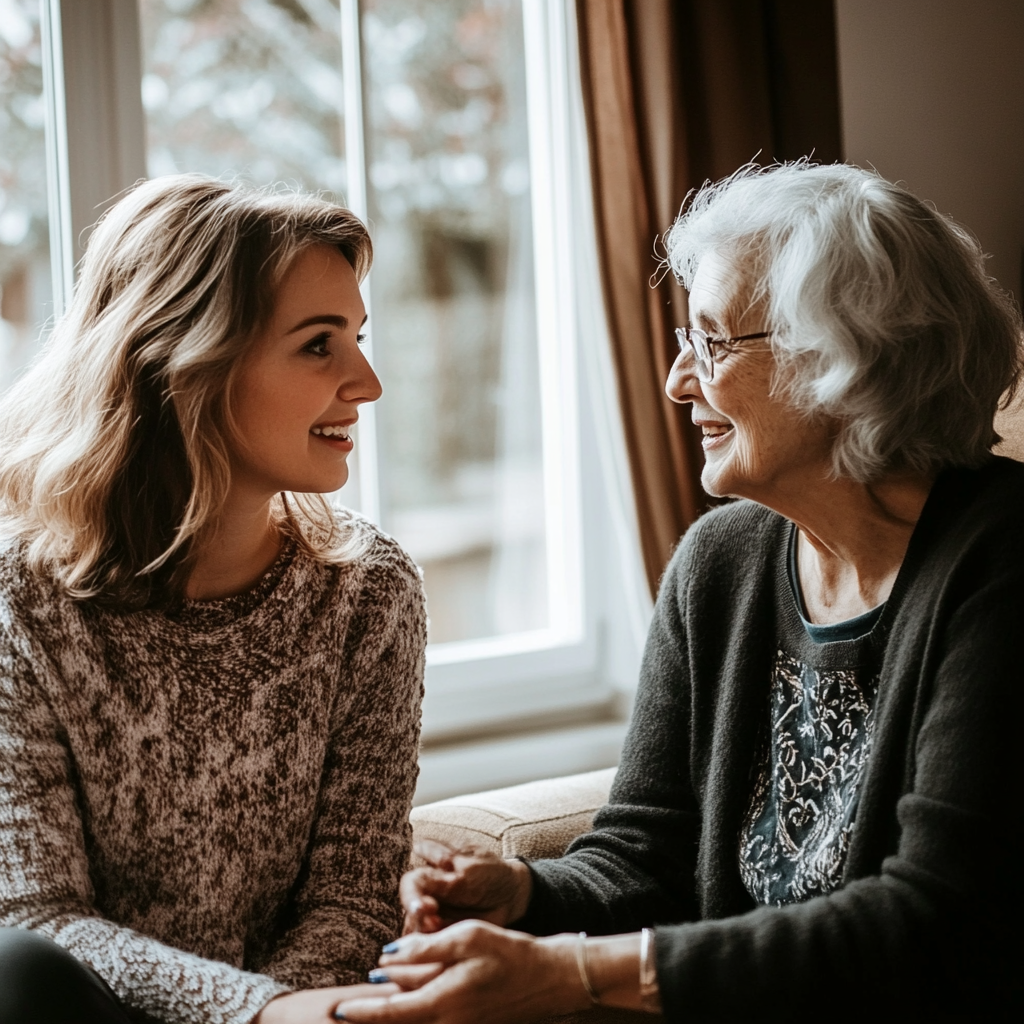

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
A voz de Mary quebrou enquanto ela falava. “Não sei o que fazer. Estou grávida, e ele diz que vai levar tudo. Ele nem acredita que o bebê é dele.”
Os olhos de Scarlett endureceram. “Não vou deixar ninguém machucar meu futuro neto”, ela disse firmemente. “Nós o faremos pagar. Você salvou essas mensagens, certo?”
Mary assentiu. “Sim, eu tirei prints.”
Scarlett pensou por um momento, então disse: “Tenho uma das escovas de dentes dele aqui. Podemos fazer um teste de DNA quando o bebê nascer.”
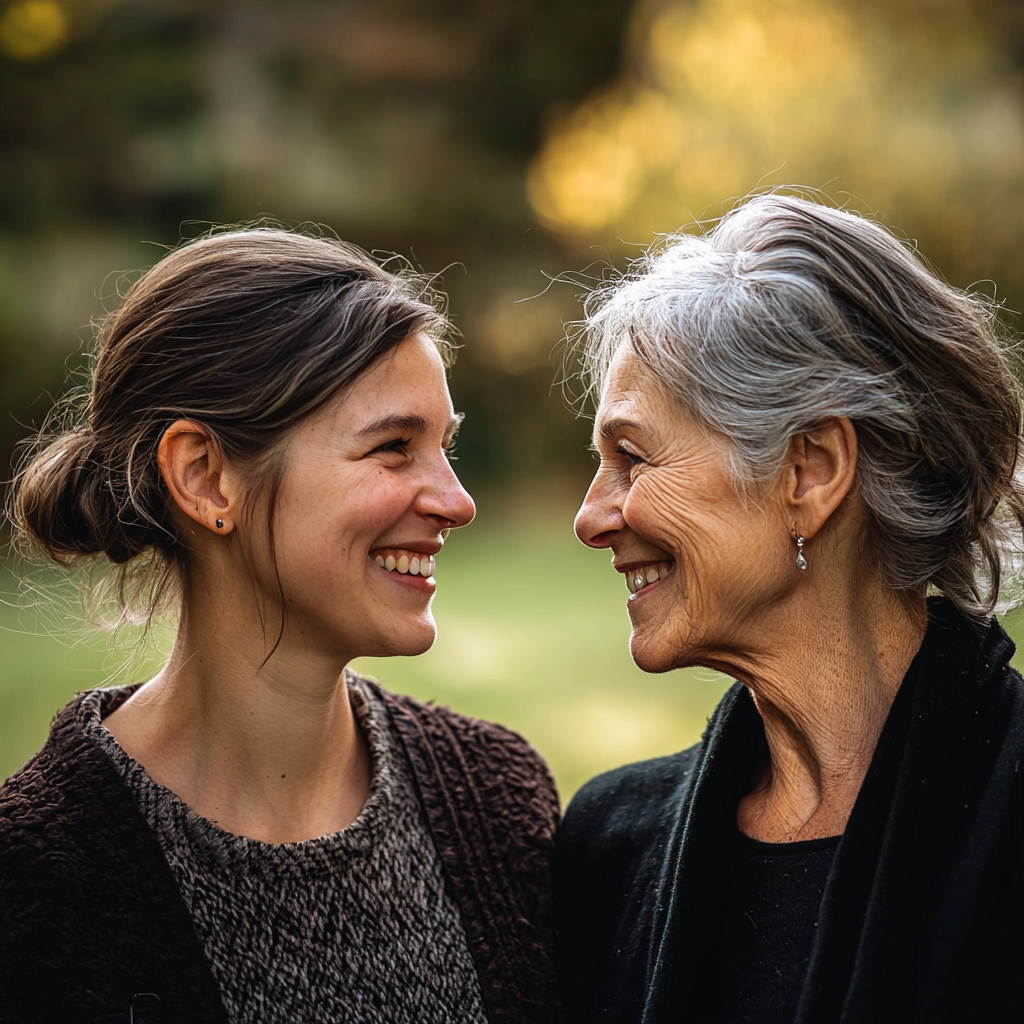

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Mary olhou para Scarlett, surpresa. “Você nunca esteve do meu lado antes. O que mudou?”
Scarlett suspirou. “Eu era uma mãe tentando proteger o filho. Mas agora vejo que preciso proteger os outros dele. O pai dele era igual — um trapaceiro. Eu suportei, esperando que Ed melhorasse. Mas ele não melhorou. E não quero que mais ninguém sofra como eu.”
Mary e Scarlett seguiram adiante com seu plano. Mary confrontou Ed diretamente e mostrou a ele as capturas de tela de suas mensagens.
“Tenho todas as suas mensagens,” ela disse, sua voz firme enquanto segurava seu telefone. “E eu já as mostrei para Scarlett. Então você não tem mais espaço para manipular ninguém.”
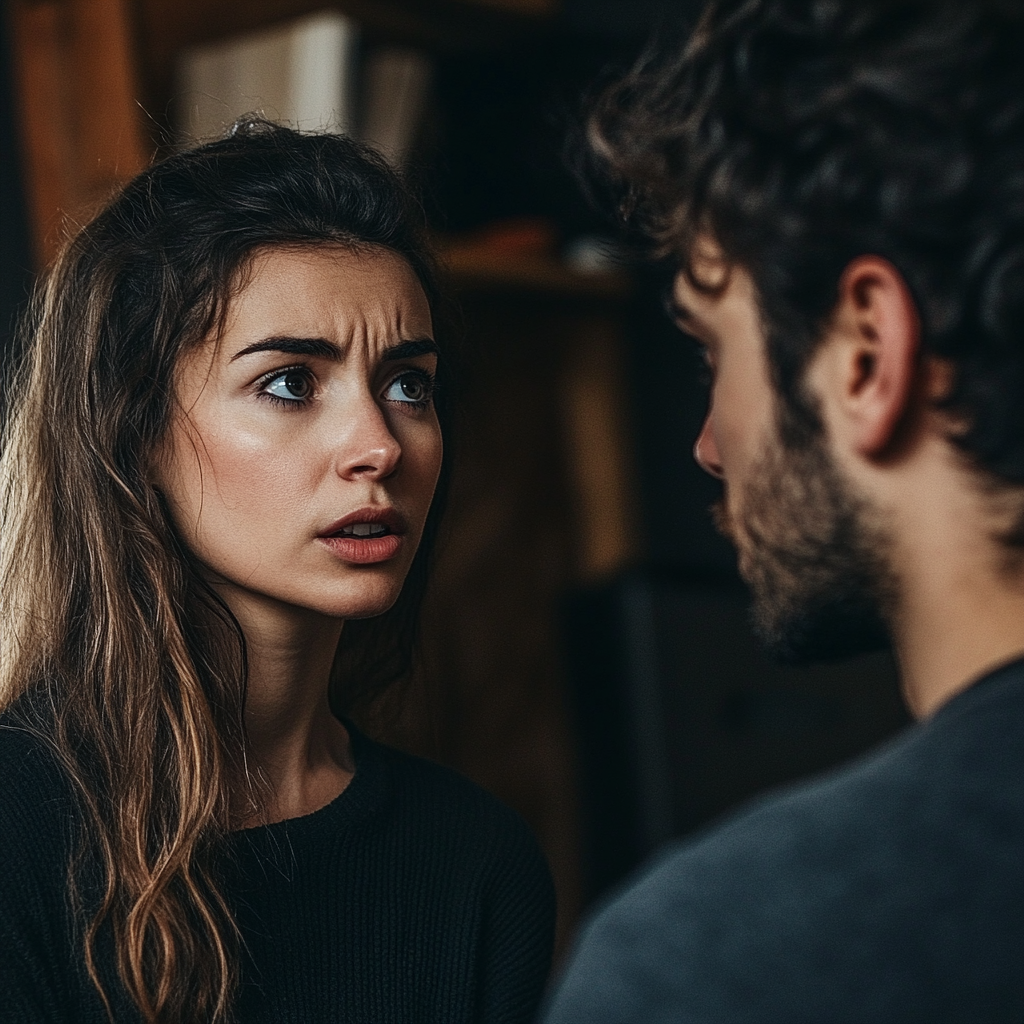

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Ed pareceu abalado, mas Mary continuou, sem recuar. “Aqui está o acordo”, ela disse a ele com firmeza. “Desista de sua reivindicação à casa, assine esses papéis de divórcio e concorde em pagar pensão alimentícia. Faça isso, e eu ficarei quieta. Caso contrário, garantirei que seu amante saiba a verdade.”
Encurralado, Ed concordou relutantemente e assinou os papéis sem dizer uma palavra. Ele não tinha ideia de que Scarlett tinha a parte final do plano.
Scarlett foi até o amante de Ed pessoalmente, revelando tudo — suas mentiras, suas falsas alegações de riqueza e seu engano. Ela não deixou nada escondido, garantindo que as mentiras do filho desabassem.
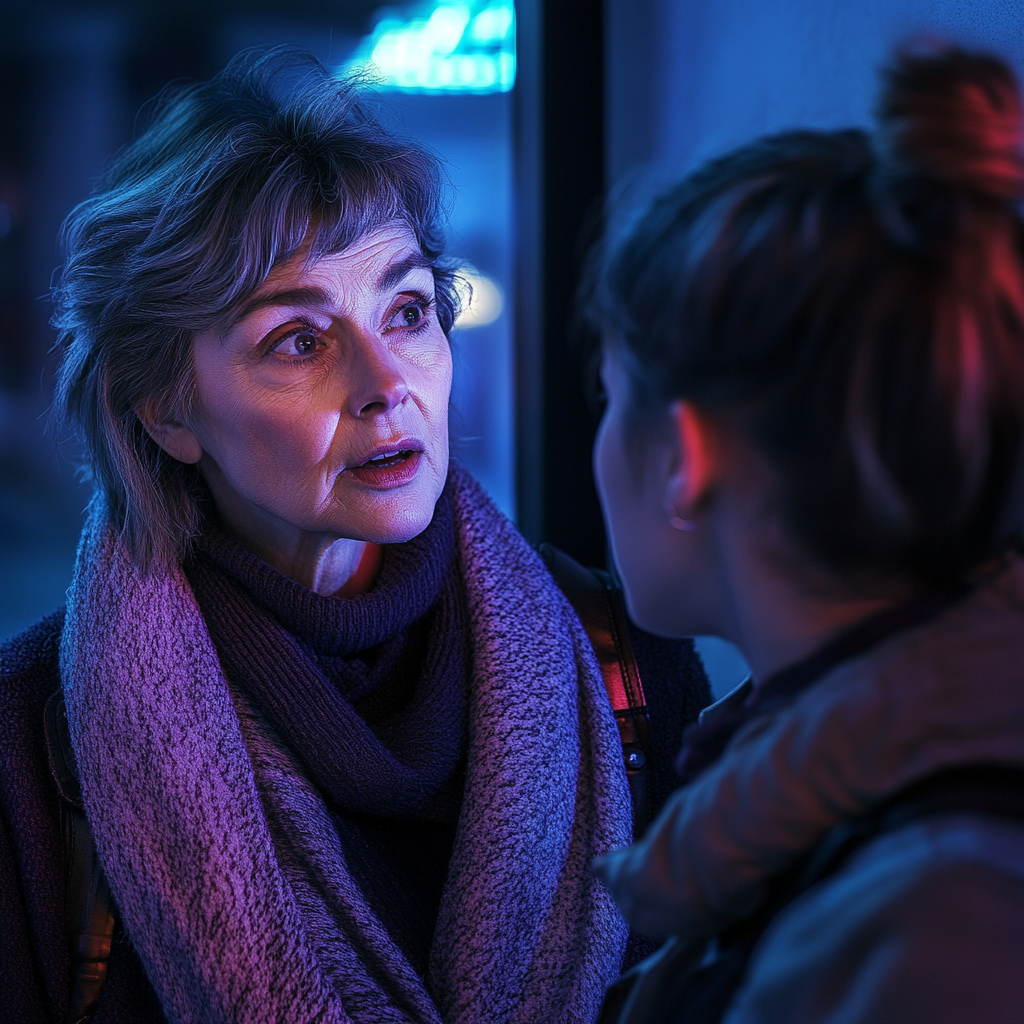

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Quando Ed descobriu, Scarlett estava sentada com Mary, tomando chá na casa dela. De repente, batidas altas ecoaram da porta da frente, seguidas pelos gritos furiosos de Ed.
“Você prometeu que não contaria se eu fizesse tudo o que você pediu!” ele gritou através da porta, sua voz afiada de raiva.
Mary olhou calmamente para a porta e respondeu: “Eu não disse nada a ela, Ed.”
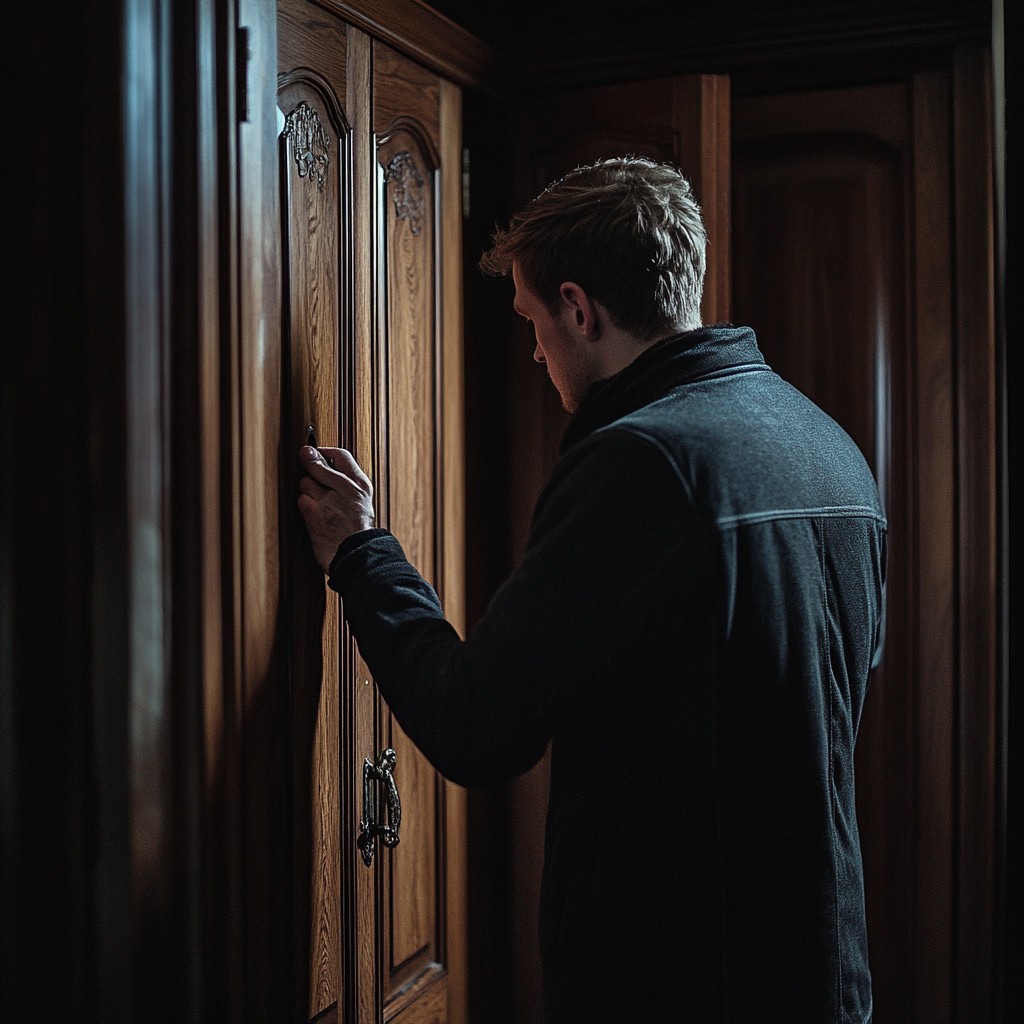

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Scarlett levantou a voz para que Ed pudesse ouvir. “Eu fiz,” ela gritou firmemente. “Eu te ensinei que mentir é errado, mas você claramente não aprendeu.”
“Vocês dois são loucos!” Ed gritou, sua voz tremendo de raiva. “Vocês vão se arrepender disso! Eu vou fazer vocês pagarem!”
Nesse momento, a polícia chegou, alertada pelo chamado de um vizinho. Eles contiveram Ed, levando-o para longe enquanto ele continuava gritando ameaças, enquanto Mary e Scarlett permaneceram dentro, inabaláveis, enquanto terminavam seu chá.
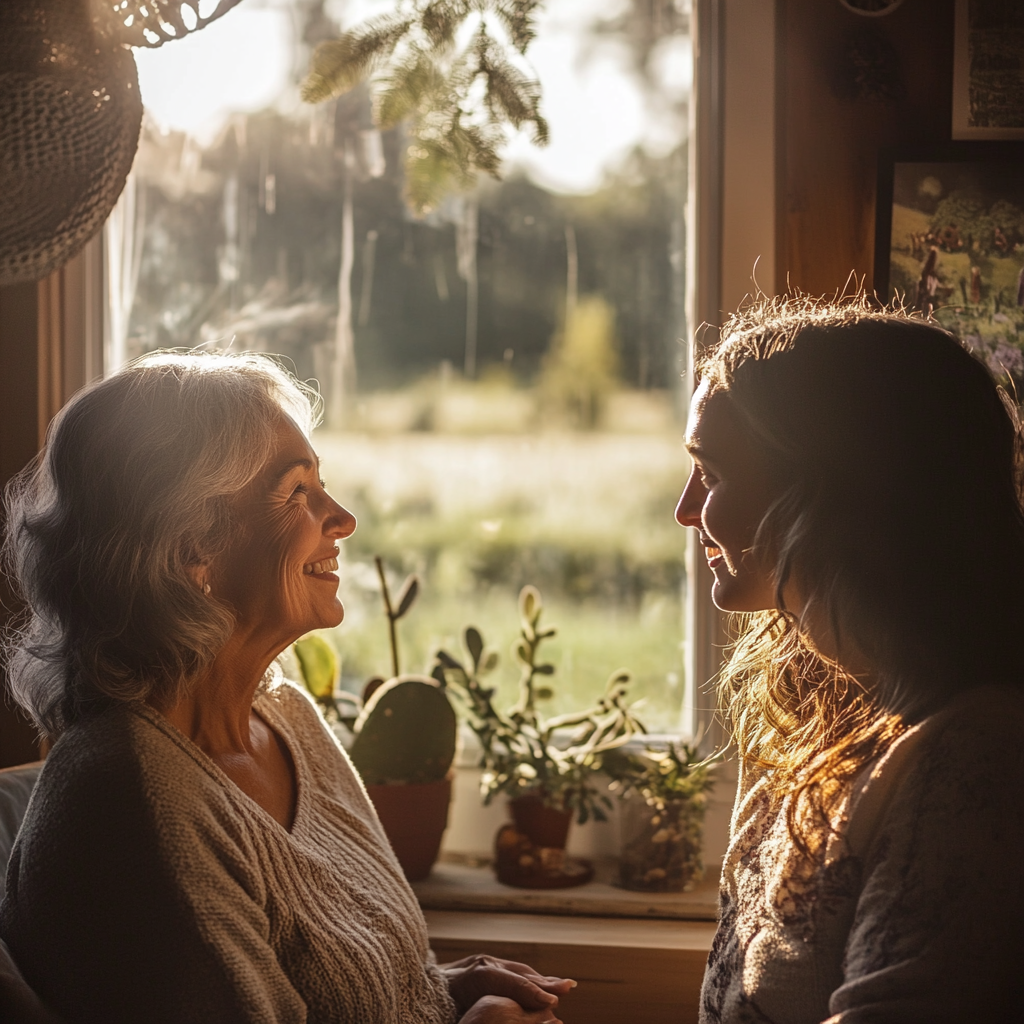

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Diga-nos o que você acha dessa história e compartilhe com seus amigos. Pode inspirá-los e alegrar o dia deles.
Se você gostou desta história, leia esta: Eric, de dezesseis anos, foge de sua família adotiva em uma viagem de acampamento, desesperado para encontrar sua mãe verdadeira e as respostas que ele sempre desejou. Mas, conforme ele enfrenta duras verdades sobre o passado e o que a família realmente significa, a jornada de Eric toma um rumo que ele nunca viu chegando. Leia a história completa aqui .
Este artigo é inspirado em histórias da vida cotidiana de nossos leitores e escrito por um escritor profissional. Qualquer semelhança com nomes ou locais reais é mera coincidência. Todas as imagens são apenas para fins ilustrativos. Compartilhe sua história conosco; talvez ela mude a vida de alguém. Se você gostaria de compartilhar sua história, envie para


Leave a Reply