
Twelve years ago, Ilya Zhirnov and Kira Cherkasova, two young women, ages twenty-five and twenty-two, respectively, disappeared from the city of Cheboksary in central Russia. Nobody knew what had happened to them until the amateur diver found their car at the bottom of the river.
The car had been underwater for almost a decade, according to the authorities.
Identity documents that survived the underwater submersion were used by the authorities to identify the two persons who went missing. Inside the car, the diver discovered two bodies along with the belongings of the young people.
This is a devastating finding, but it may offer new information about the case.
The first theory put up by the police states that nobody saw or reported the couple’s accident to the authorities after they lost control of their automobile on the slippery road and ended up in the river.
However, many are interested in learning how long it will take the authorities to determine with certainty what happened to the two individuals. Will an investigation into this matter be launched?
Is there any chance that this finding may lead to the finding of more clues or evidence that will clarify what happened twelve years ago?
It’s uncertain what more research will reveal for the time being.
It’s uncertain what more research will reveal for the time being.
However, the amateur diver’s discovery indicates that we shouldn’t give up trying to solve our problems. It can be a significant development for individuals searching for information in cases of missing persons or unsolved murders.
Ultimately, this discovery should prompt us to consider the individuals who are still missing and act as a reminder that sometimes the answers are right in front of us.
What the Acne on 8 Body Parts Is Trying to Tell You About Your Lifestyle Habits
Acne really can determine what happened to your body and what health problems you may have. But in most cases, it is all caused by very simple lifestyle matters that can easily be changed right away. The thing to do is to figure out what triggered another pimple and what we can do today to prevent it from occurring in the future.
We at Bright Side have checked out the causes and would like to share this useful knowledge with you that’ll change your life from now on. But please keep in mind that this article is for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor before you take any action or treatment.
1. Around the mouth
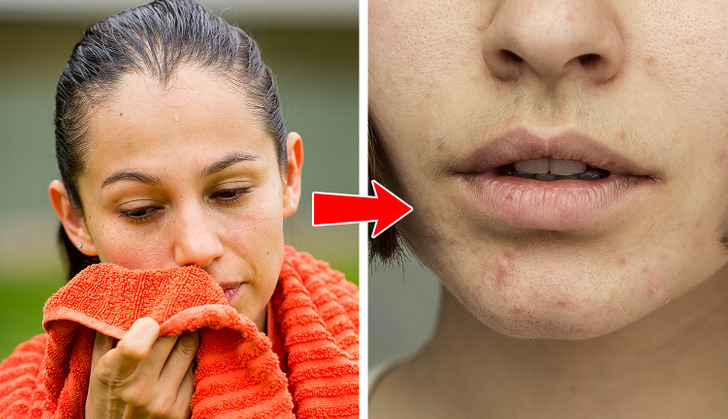
Acne around your mouth can occur if the skin in this area is irritated or frequently touched, like, by a cell phone or some other objects like helmet straps or musical instruments. Different cosmetics and facial products might also be the cause. As well as hormones and genetics.
First of all, if it appears frequently, see a dermatologist who will find a proper treatment that will work for you. But in any case, it’s always better to prevent it rather than to cure it. So make cleaning your skin with a gentle or mild cleanser twice a day a routine. Use makeup labeled as “non-comedogenic” (non-pore-clogging) and oil-free products, and please avoid touching your face.
2. On the nose
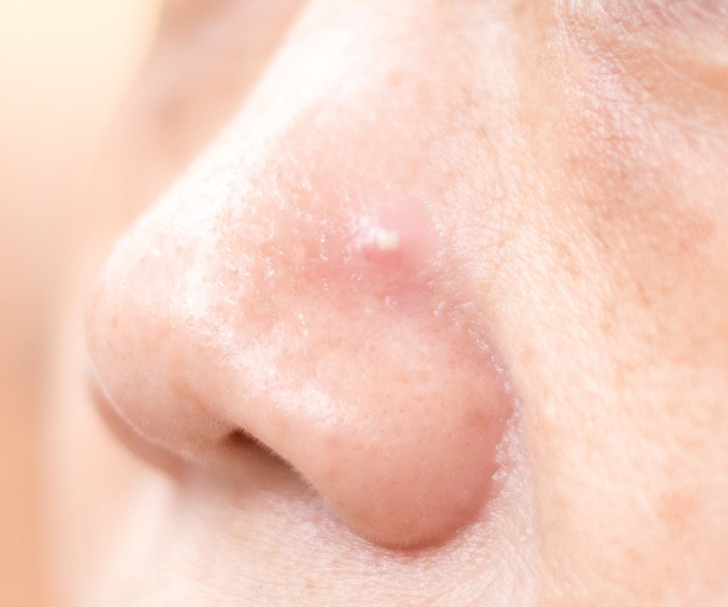
Our nose is one of the most common areas of the face to develop acne. It’s because its pores are typically larger, which makes it easier for dirt and bacteria to clog them up. What’s more, the skin here is also oilier and consequently more vulnerable to acne.
Nose acne can be triggered by diet, stress, and certain medications. Sometimes it can be a sign of more serious underlying health issues. But the most common cause is poor hygiene. So it’s always good to add some Tea Tree Oil to your routine, which is a very gentle and effective treatment against acne, or sodium sulfacetamide and sulfur which will prevent bacteria on the skin from multiplying. In very severe cases, consult a dermatologist.
3. On the forehead
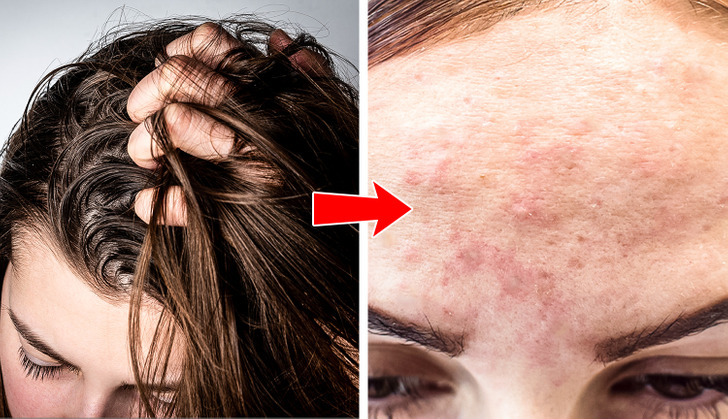
The significant factor here is the same — an increase in oil production on your skin. But sometimes, it’s hard to figure out why it happens. Especially if you don’t take certain medications, and it’s not hormones or stress. It is interesting to know that our hair can be the source of forehead acne.
If your hair is oily, the oil can get on your forehead and clog its pores. Different pomades, gels, and waxes also may be the cause as they often contain cocoa butter or coconut oil and can leave your skin extra oily. A gentle cleanser can solve this problem. If it doesn’t help, try to avoid any oily hair products and just wash your hair more often.
4. Jaw and neck
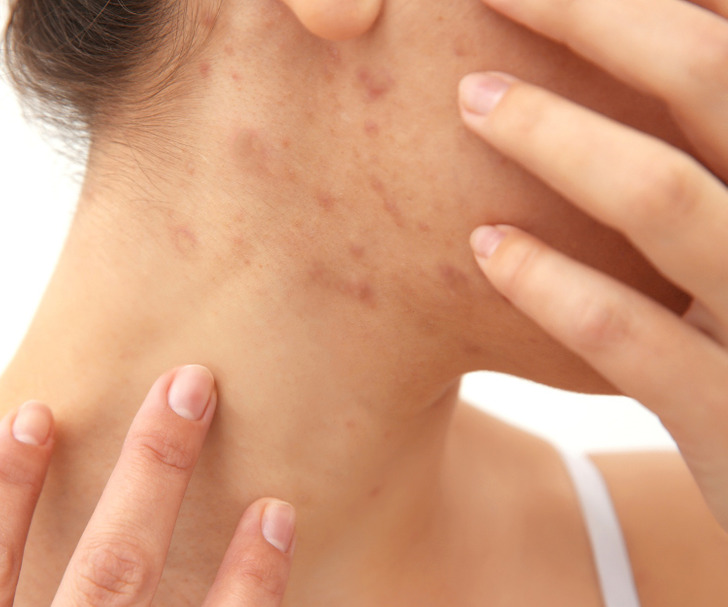
If you think that acne, in general, may be hormonal, there’s good news for you: it’s not all like that. When certain hormone levels change, it can lead to increased androgens — the common contributing factor to adult acne. But there are some areas that are true indicators of hormonal fluctuations, and they include our jaws and neck.
It’s completely okay if fluctuations happen during menstrual cycles. It can also be caused by taking medications like birth control. In severe cases, it may be a medical condition, but most of the time a non-comedogenic cleanser, moisturizer, and acne treatment can solve the issue. Just like basic sun safety and proper sunscreen use.
5. On cheeks
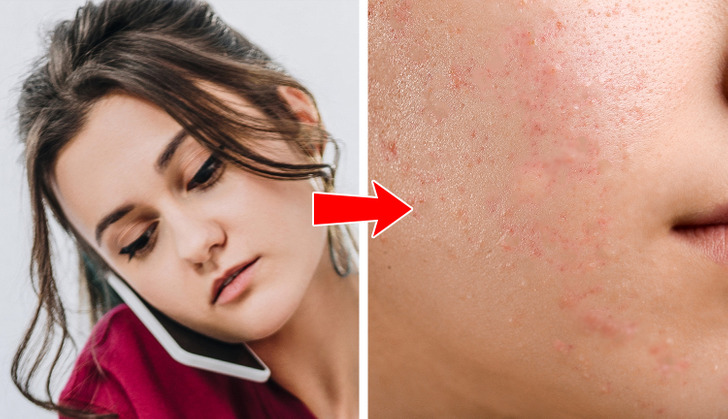
Cheek acne is also a very common problem, especially now that we all have cell phones. Yes, not just touching your face, but even a mere phone conversation can cause some pimples to appear in this area. Phones are great at spreading bacteria. As well as dirty pillowcases and sheets and other objects that come into contact with your skin.
Cheek acne may be hormonal. But it is way more possible that it’s being caused by certain lifestyle habits. So this time, everything can be solved by a few simple changes. Like wiping down your phone before each use and not taking it to any germy places like the bathroom. Changing pillowcases and sheets every week is also a good idea, just like washing your hands regularly.
6. On your back
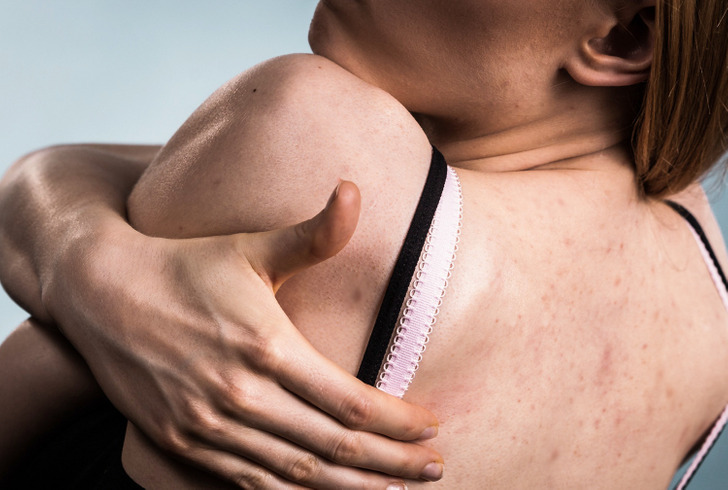
Back acne can be a mere allergy to sunscreen, moisturizer, body creams, massage oils, and wax. It also may be caused by our sweat, which mixes up with oil and toxins on our skin and clogs the pores. That’s why a quick shower after training is so important. And a proper washing of your back is a must.
Dirty clothes, blankets, and pillows can become a major cause of back acne as well. Clothes that are too tight are also a bad idea. They don’t allow your skin to breathe, which can cause irritation and, consequently, pimples on your back. If there is no obvious outer cause, it is better to pay attention to your diet and check to see whether you are getting sufficient nutrients. Stress could be the cause here too.
7. On legs
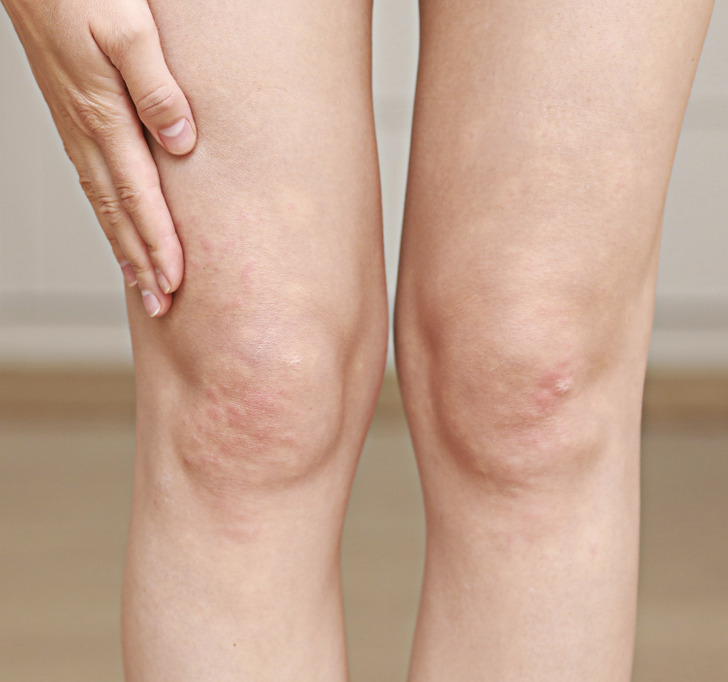
Acne is mainly the result of bacteria, sebum, and dead skin cells trapped in hair follicles and clogging the pores. It leads to inflammation and, on the legs, is entirely a physical issue. It’s typically caused by some athletic equipment rubbing against your skin or clothing or undergarments that are too tight.
But be cautious. People can often confuse acne on their legs with similar conditions as folliculitis, eczema, or keratosis pilaris. So if it is itchy and painful, it’s better to consult a doctor and use a professional treatment.
8. On your chest
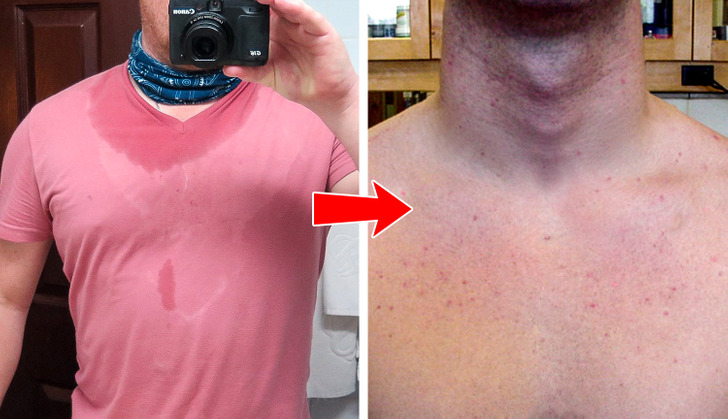
Chest acne develops for pretty much the same reasons as on our backs and legs. For instance, if you have sensitive skin, harsh laundry detergents can clog and irritate your hair follicles. So it is better to choose sulfate- and fragrance-free hypoallergenic products when planning your next washing routine.
Wearing clothing that is too tight, or that doesn’t breathe well during your athletic training also can trap sweat, oil, and bacteria in the pores of your skin. This can also happen as a result of using certain body lotions that contain pore-blocking ingredients. So make sure to look for fragrance- and oil-free versions next time. They are usually labeled as non-comedogenic, which means they don’t clog pores.
What other methods do you use to prevent acne on your face and body? Have you managed to do it by changing only certain lifestyle habits?
Preview photo credit natali_ploskaya / Shutterstock.com, anastas_ / Depositphotos.com



Leave a Reply