If you’ve ever explored your grandparents’ house, you’ve probably found some strange items that left you puzzled.
Recently, someone online shared a photo of some metal tools that, if it weren’t for the nut-shaped bowl they’re in, could be mistaken for tiny weapons.
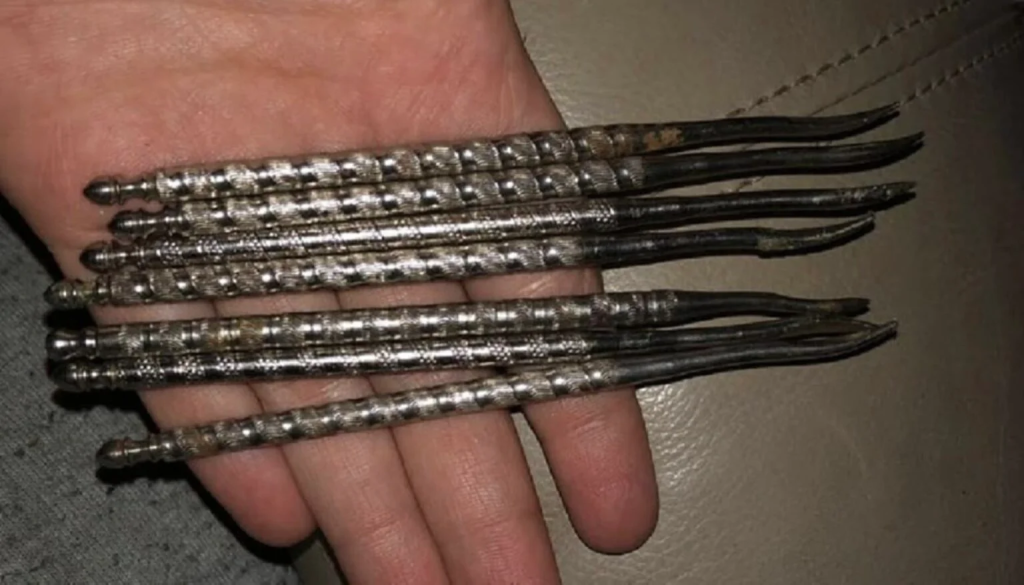

People online quickly started guessing what these odd tools were for, with one person even joking that they might be used to “find cavities.” Curious to know more about this mysterious tool? Keep reading!
Most of us have heard of a nutcracker—not the ballet with the Sugar Plum Fairy, but the metal tool used to crack open nuts.
A nutcracker looks like pliers and usually has two metal arms with a hinge at the top. The arms are often serrated to grip the nut better. You place the nut in the jaws of the nutcracker, squeeze the arms together, and the shell cracks open, revealing the nut inside.
Nutcrackers come in all sorts of designs and sizes, from simple handheld ones to fancy, decorative pieces.
Some are made for specific types of nuts, while others can handle a variety of nuts and even shellfish like lobster or crab.
Getting the nut out of its hard shell isn’t always easy. After cracking the shell, you still have to deal with the meat sticking to the tough walls inside.
That’s where a nut pick comes in, which is the tool that’s confusing people online.
Nut picks come in different styles and materials, like metal, wood, or plastic. Some even have fancy handles or are designed to be comfortable to use.
They’re useful for enjoying all kinds of nuts, such as walnuts, pecans, and almonds, where you need to get the edible part out of the shell.
People online have been sharing their experiences with these versatile tools.
One person remembered the hard work of cracking nuts in the past, saying, “We used them for walnuts. Back then, you didn’t buy pre-cracked walnuts for baking; you had to crack them open yourself.”
Another user shared, “We used them for walnuts, pecans, and more. They came with the nutcracker and were also great for getting lobster out of those tiny legs.”
Someone else mentioned, “They’re crab and lobster meat picks. I’m lucky to still have my family’s set. Growing up near Maine, we had lots of chances to use them!”
Another person added that she’s found multiple uses for the pick, saying, “I’ve used them for their intended purpose, but as an artist, I’ve also found other ways to use them.”
Others had different ideas. One user said, “They’re called olive picks, but you can use them for other things, so your hands don’t touch the food.” Another joked, “Mostly used to pick your teeth after a big dinner… also handy for finding cavities!”
What are your favorite memories of using nutcrackers and picks?
Share your thoughts in the comments and spread the word so we can hear from others too!
Why Blake Lively and Ryan Reynolds Weren’t at 2024 Met Gala
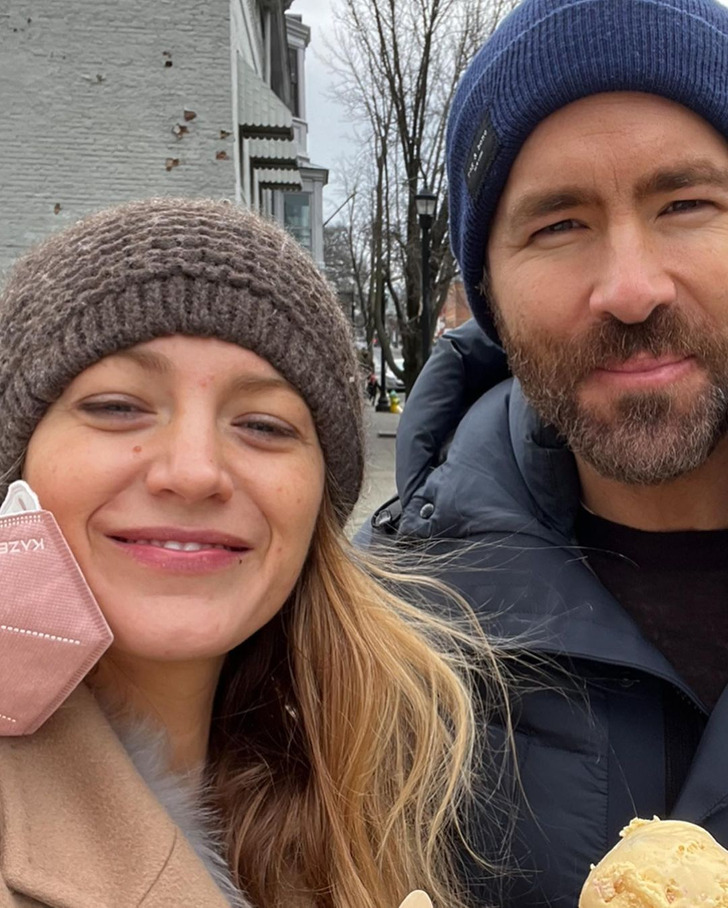
The 2024 Met Gala is a wrap, but let’s be real, it was missing some major players this time around. Like, where was Blake Lively, the ultimate Met Gala royalty? She and Ryan Reynolds ghosted the event for the second year straight, and fans are totally bummed about it.
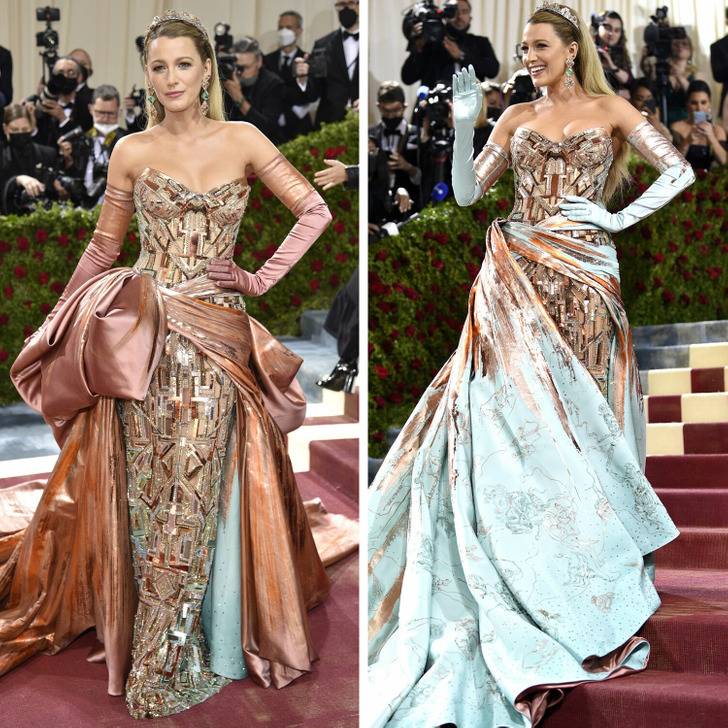

Blake Lively and Ryan Reynolds ended up skipping their second Met Gala in a row. Instead of hitting the town for the “Sleeping Beauties: Reawakening Fashion” themed bash, Blake and Ryan opted for a cozy night in with their four kiddos. Family time over fancy parties—it’s hard to argue with that!
Lively sparked hope she could attend the Met Gala when she went to a Tiffany & Co. event in New York last week. Ultimately, she let that be her big fashion moment for early May.

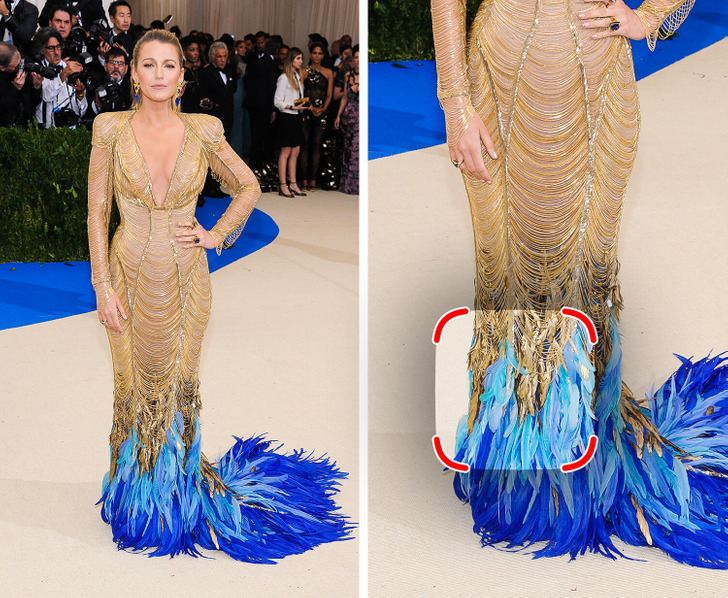
Blake Lively has quite the Met Gala history, even poking fun at herself for perfectly coordinating with the carpet in previous years. Her last Met Gala appearance was in 2022, where she not only attended, but also co-chaired the event. Embracing the “Gilded Glamour” theme, she stunned in an Atelier Versace gown paired with her signature Lorraine Schwartz jewelry and a tiara.
What sets Lively apart is that she styles herself, even for major events like the Met Gala. She explained that she enjoys the creativity and control it offers.

Fans were eagerly anticipating Blake Lively’s return to the 2024 Met Gala, hoping for her signature style and charisma to grace the event once again. However, when she didn’t make an appearance, disappointment swept through social media. “Blake Lively, where are you?” one fan questioned, echoing the sentiments of many who were eagerly awaiting her presence.
Another fan expressed their disappointment, saying, “pretending to not care Blake Lively isn’t there to save the night #MetGala.” It’s clear that Lively’s absence left a noticeable void for many attendees and followers of the event, underscoring her significant impact and presence at the Met Gala over the years.
Check out Blake’s top Met Gala looks of all time!


Leave a Reply